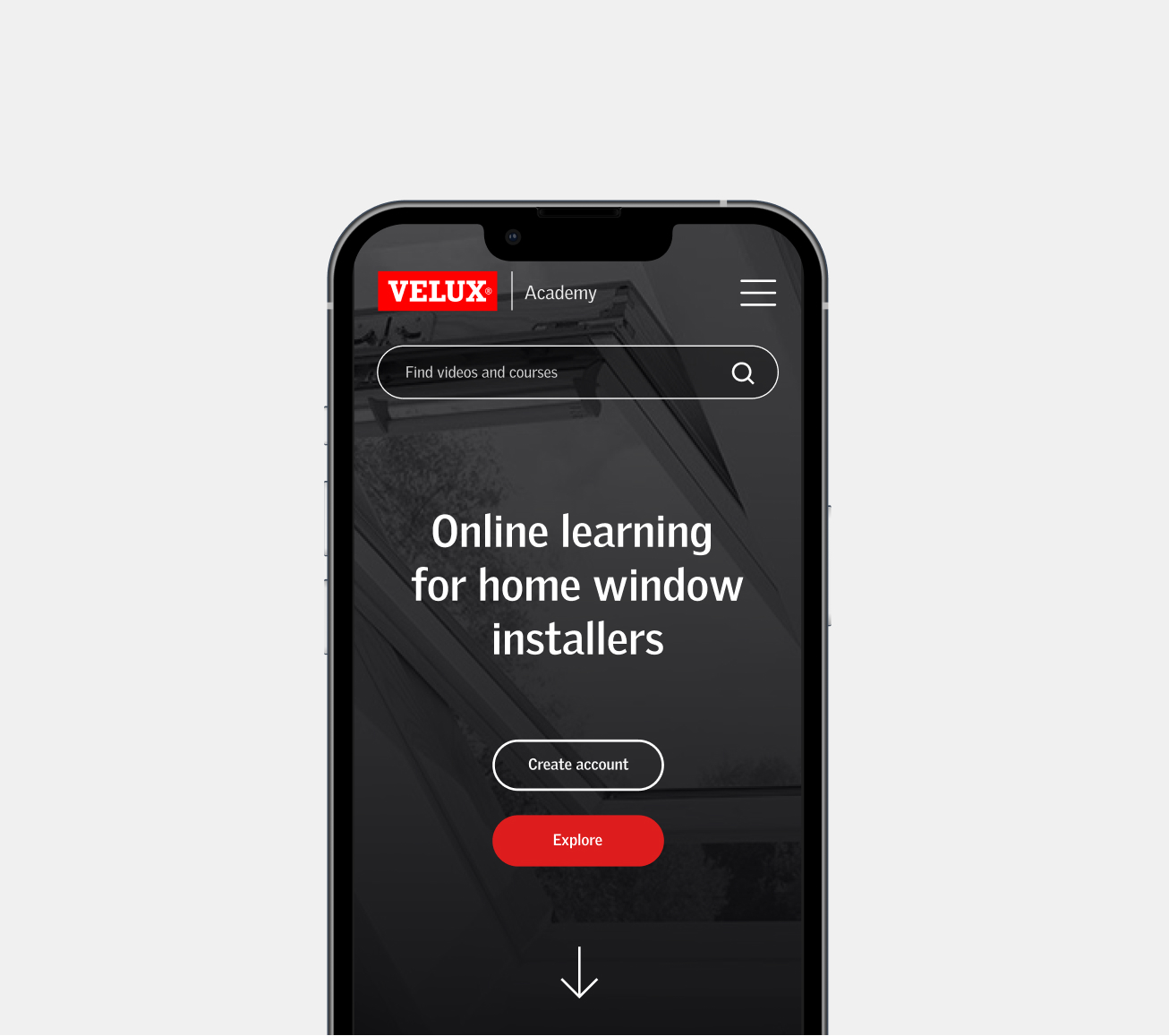
Understanding your users through UX research is the first step to creating successful experiences.
By putting ourselves in the shoes of your customers, we help your brand create engaging experiences and successful products.
Approach
Variant team of researchers will give your brand deep insights about your audience. We can optimize your marketing campaign, test the effectiveness of your digital products, or improve the usability of your design. But most importantly, we help you understand what are the drivers that make your clients love your brand.
Marketing & analytics✕
Tools to achieve marketing success by improving the user experience.
Conversion rate optimization (CRO)
Conversion rate optimization (CRO) is the practice of increasing the conversion rate of a marketing campaign. Marketers use CRO to maximize the number of users who take specific actions on websites, landing pages and social channels. Examples of desired actions include: purchasing products or adding items to the cart, subscribing to newsletters, requesting information, or simply clicking a call to action. CRO is not just about the numbers. Quality plays a big role in the results of a marketing campaign. In recent years, conversion rate optimization has evolved. Along with the traditional quantitative approach, marketers are now seeking a deeper understanding of users, their core motivations, and the UX barriers that prevent them to act.
A/B testing
A/B testing is often used in combination with conversion rate optimization. With A/B testing, researchers test two or more variations of the same message at the same time. Each variation is identical to the others, except for a single variable. This approach allows researchers to better understand which message is the most effective. The process is often repeated many times to constantly improve the results. A/B testing can be used to increase the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, or in general, to improve the performance of the user experience.
Clickstream analysis
Clickstream Analysis keeps track of the sequence of actions that users perform on the website. Clickstream Analysis helps researchers find the most visited sections of a web site, entry points and exit points, the logical sequence of the visitor's actions, or the keywords that the user typed to find the web site. Our research team analyzes the clickstream to get deep insights about users, generate user profiles, or identify areas of the user experience that need improvement.
Heatmap analysis
Heatmaps are data visualization tools that record how the user clicks, scrolls, and moves the mouse on pages. Heatmaps represent the time spent in specific areas of the website by using different colors. Heatmap analysis is often used in combination with other techniques, such as clickstream analysis and A / B testing. Since in a desktop environment users "thinks" with the mouse, heatmaps help to better understand their underlying mental processes. In particular, they are useful for pinpointing distracting elements or items that generate confusion.
Usability✕
Fine-tuning the user experience to improve usability.
Task analysis
One of the core activities of UX design is to clarify the problems faced by users and then design effective solutions. Task analysis is performed at the start of every new project. It can identify opportunities for improving the user experience. Starting from the audit of the user interface, researchers generate a schematic representation of the steps that users must take to complete the target objectives. The diagram splits the user experience in several small steps. Researchers analyze each step to find usability issues and opportunities for improvements.
Card sorting
Card sorting is a preliminary activity that helps designers understand the information architecture of a website, web app or application. Card sorting if performed by a group of people. Researchers create a set of topics, and participants must regroup the topics in a way that feels most natural to them. Each group is then labeled with a name and a description. The resulting classification is then confronted with the current information architecture to assess its effectiveness.
First click test
The first click test checks the usability of an interface by measuring how easy it is for the user to complete a simple task. Its name is "first click" because it tests if users will indeed click the target element without hesitation as their first interaction. It helps researcher verify that specific elements of the user experience, such as buttons or forms, work as expected. It is often performed in combination with heatmap analysis, but it can also be used as a standalone tool while creating the wireframes.
Tree testing
Tree testing validates the explanatory power of menus, tabs, sections, or other category structures. It is often used together with card sorting. During the test, researchers create a document containing the hierarchical structure of the site and its menus. The document is then presented to a group of participants. Participants are asked to state where in the tree they expect to be able to find a particular piece of content. Comparing the results with the actual website structure will help identity misplaced or mislabeled content.
In person usability test
Usability tests allow researchers to observe the interaction between the user and the interface in a controlled environment to test its usability. The testing activity requires several steps: creating a testing hypothesis, designing a testable prototype, selecting users, interviewing them, and writing the final report. Tests can be moderated or unmoderated. In a moderate test, the interviewer interacts with users to guide them, or to investigate the motivations that push them to act. Unmoderated tests do not require any interaction; they can therefore be performed "in parallel" on many users.
Remote usability test
In a remote usability test, users and researchers are located in different places. Users navigate the interface without interacting with the researcher by executing a list of predetermined tasks. Users are required to "think aloud" to explain the mental processes that lead to their actions. Remote testing allows researchers to involve a greater number of subjects and to reach people located in very distant places. It also the preferred tool for interacting with people with mobility problems. Remote usability tests are great for testing digital interfaces. Instead, they are not suitable for hybrid environments such as virtual reality, geolocation, or voice interfaces.
User discovery✕
We listen to your clients to design better products, faster.
Focus groups
Focus groups are informal, collective interviews that help researchers focus on the needs of a target audience. A focus group does not capture statistical data. It does not give a comprehensive profile of a particular audience. Rather, it is an orientation tool that delivers ux designers and ux researchers a qualitative perspective on how the audience interprets a certain issue. Our focus groups are generally made up of 6-9 people; we take care of identifying candidates, preparing the script, moderating the execution, and delivering a final report.
In-depth interviews
In-depth interviews can be used as an alternative to focus groups. Compared to collective interviews, they differ in many aspects. In-depth interviews investigate a user's individual experience. Since no group dynamics are present, the interviewer and the user can speak more freely. In-depth interviews are better tools to investigate a user's perspective. However, they they are usually more time-demanding compared to focus groups.
Ethnographic research
In ethnographic research, researchers observe people's behavior in their natural environment. The researcher observes actions and interactions without directly influencing the observed people. The lack of interaction allows to gather qualitative insights into audience priorities. Ethnographic research is often used to evaluate hybrid experiences (phygital design) because it gives researchers the chance to observe how the user interacts with the surrounding environment.
Expert interviews
During an expert interview, researchers consult stakeholders who possess relevant knowledge in the field. Stakeholders can be industry experts, external consultants, persons of interest, or project managers in the company. Expert interviews are an ideal complement to audience interviews (or focus groups). The former offers information on the "state of the art" in the industry, while the latter gives insights on users perspective.
Participatory design✕
We engage users in the design process thought workshops and remote collaboration.
Co-creation
Co-creation is the practice of collaborating with users and stakeholders during the design process. Instead of forming generic assumptions about users by building buyer personas, co-creation brings the voice of the audience directly into the creative process. We can organize co-creation sessions for your brand. During each session, a diverse group of stakeholders contribute to the creative development under the leadership of an experienced moderator. Insights gained during the co-creation phase will will help designers create a product closer to the real needs of the audience
Remote co-creation
In times of technological acceleration, co-creation is also evolving, opening up new possibilities for design researchers. Remote co-creation achieves the same goals as traditional co-creation, but uses advanced prototyping tools. The main advantage of remote co-creation is the ability to engage
Preference testing (A/B testing)
Preference testing is a simplified version of co-creation where stakeholder interaction is more limited. Participants are asked to express a preference between different versions of a prototype. Participants must give a motivation for their choice. Researchers will then ask additional questions to capture more insights about users' choices.
Co-creation facilitation
Co-creation is an increasingly popular activity among product development teams. Product teams often benefit from experienced external facilitators. A good facilitator will guide a diverse team of people toward a common goal in a productive way. Facilitators have in-depth knowledge of design and co-creation processes, can manage group dynamics while avoiding common pitfalls, and can ensure a superior creative outcome.
UX research strategy✕
A perfect research strategy brings better products and a higher ROI.
UX research programs
Understanding your audience is the first step to creating successful products. Making generic assumptions about users' needs is a very common practice. Unfortunately, a superficial approach puts the brand at risk of delivering subpar experiences. UX research programs are an ideal complement to customer experience design. UX research can deliver essential feedback before, during, and after the design process, substantially improving the project's likelihood of success.
UX audit
A user experience audit is conducted by a team of designers and senior researchers. UX audits highlight areas of improvement in a customer experience. It can be used to identify problems within the user interface, or to find critical issues in the customer conversion process. The UX audit gives detailed recommendations for a wide range of aspects, including: strategy, value proposition, conversion optimization, customer care, sales effectiveness, web analytics, user engagement, interface usability, conformity to best practices, information architecture, user flow.
Competitors UX analysis
An important research tool that is responsible for gaining insights into the competitors user experience . Competitor analysis is particularly useful for identifying gaps between a brand and its competitors. It can be used as a preliminary research tool to gain insights into the state of the art and get inspiration. In later stages, it is useful to validate the quality of the brand's user experience.
Customer journey mapping
Our user researchers study customer behaviors through a mix of qualitative and quantitative data to identify their decision path. We identify all the touchpoints of the experience and, for each of them, study the most appropriate interactions. The final object of customer journey mapping is maximizing the conversion of the potential customer.
End to end validation✕
Early and frequent product tests are the key to design better products, faster.
Five second testing
Recent studies have shown that a user needs only three to five seconds to judge the usefulness of a web page. Slow or cluttered interfaces have less chance to capture the audience's attention. The five-second test if a design can communicate the right message fast enough. Researchers show the user an image for five seconds. The user must then answer questions by recalling the user interface. Five-second testing is useful for testing design usability, message clarity, and brand memorability.
UX design surveys
A test format that captures feedback on websites, animations, apps, or graphic concepts. During the survey, researchers show the design to the audience, and then ask a series of questions. The questions can take the form of qualitative surveys, by means of open-ended questions, or quantitative surveys, using multiple-choice questions. Design surveys are an excellent complement to five-second tests. Unlike the latter, the during the survey user has the opportunity to inspect the design throughout the session.
Iconography audit
The iconography audit tests the effectiveness of the icons in a user interface. The icons in the interface must be easy to identify, have a clear meaning, and be logically consistent. Tests use two different modes of evaluation. At first the icons are evaluated "out of context" i.e., isolated from the original context. Then, they are evaluated inside the user interface.
If you’re interested in any form of collaboration, please send us an email and we’ll get back shortly.
info@variant.design